The new model cells aid in the study of early embryonic development.
Professor Vincent Pasque and his colleagues at KU Leuven have used stem cells to create a new kind of human cell in the lab. The new cells closely mirror their natural counterparts in early human embryos. As a result, scientists are better able to understand what occurs just after an embryo implants in the womb. The was recently published in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
A human embryo implants in the womb around seven days after fertilization if everything goes correctly. Due to technological and ethical constraints, the embryo becomes unavailable for study at that point. That is why scientists have already created stem cell models for various kinds of embryonic and extraembryonic cells in order to investigate human development in a dish.
From left to right: Bradley Balaton, Thi Xuan Ai Pham, Amitesh Panda, and Vincent Pasque. Credit: KU Leuven
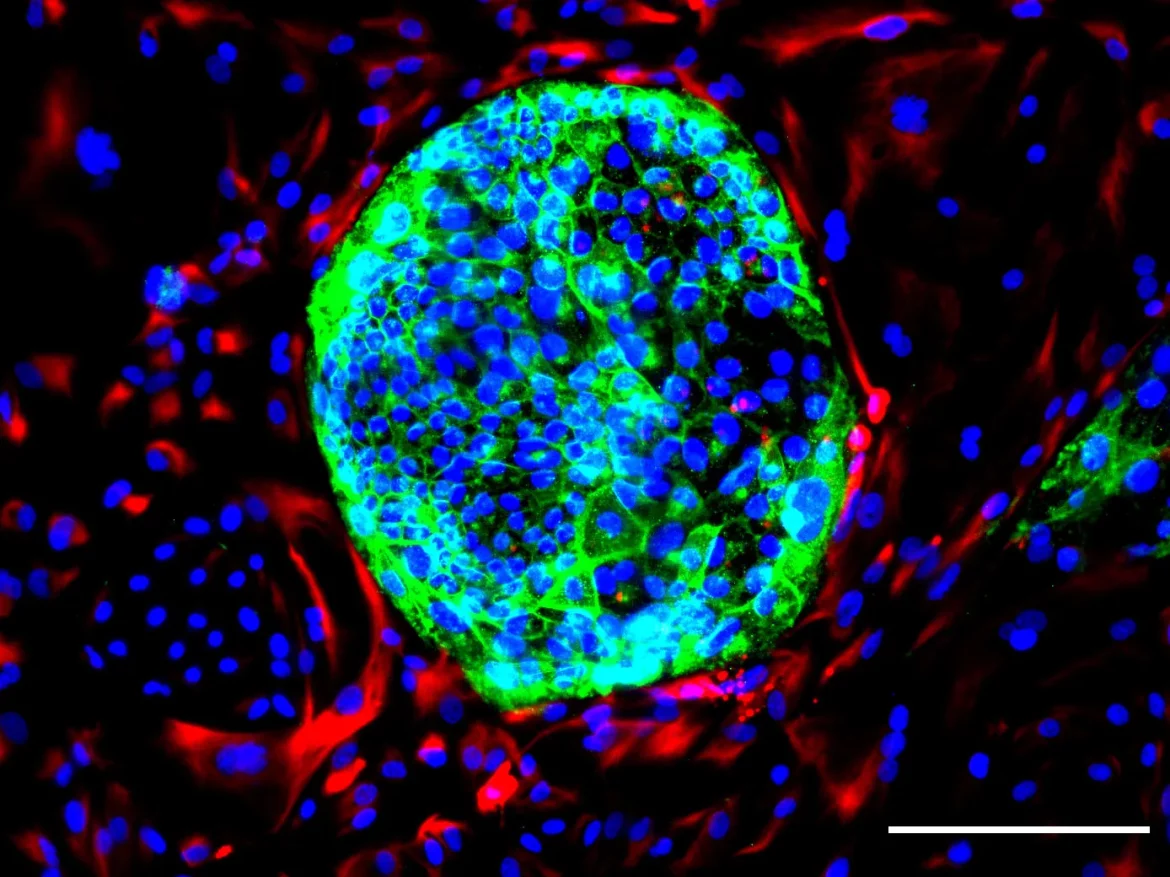
Vincent Pasque’s team at KU Leuven has developed the first model for a specific type of human embryo cells, extraembryonic mesoderm cells. Professor Pasque: “These cells generate the first blood in an embryo, help to attach the embryo to the future placenta, and play a role in forming the primitive umbilical cord. In humans, this type of cell appears at an earlier developmental stage than in mouse embryos, and there might be other important differences between species. That makes our model especially important: research in mice may not give us answers that also apply to humans.”
The model cells were created by the researchers using human stem cells, which can still grow into all cell types in an embryo. The new cells closely resemble their natural counterparts in human embryos and hence serve as an excellent model for that cell type.
“You don’t make a new human cell type every day,” Pasque continues. “We are very excited because now we can study processes that normally remain inaccessible during development. In fact, the model has already enabled us to find out where extraembryonic mesoderm cells come from. In the longer term, our model will hopefully also shed more light on medical challenges such as fertility problems, miscarriages, and developmental disorders.”